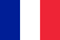
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis, is a common infection that affects the nail plate, nail growth zone and nail bed and is the cause of yellow toenails. The violation may seem like only a cosmetic problem, but if treatment is not started in a timely manner, it can lead to changes and destruction of the nail plates, as well as more serious complications.
We'll tell you what kind of infection this is, whether it can be cured and how to understand that there is a fungus on your toenails.
What is onychomycosis and the reasons for its occurrence?
Onychomycosis is a fungal infection. In most cases, nail fungus is caused by microscopic fungi of the dermatomycetes group. In particular, we are talking about:
- Trichophyton rubrum;
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes;
- Epidermophyton floccosum.
Less commonly, infection can be caused by yeast and mold fungi.
How it enters the body:
Nail infections occur when the pathogen enters the nail plate or other nail structures. Typically, fungi affect the nail in one of three ways:
- through the subungual notch - the area where the nail came out of the nail bed, and now there is a small distance between it and the tip of the finger;
- through the dorsal, or upper, part of the nail plate;
- through the proximal nail fold, which is located at the base of the nail root.
Sources of infection:
The exposure itself occurs through contact with the environment through various objects. For example, through bath mats, washcloths, scissors and other manicure accessories, as well as in closed shoes, where humidity and heat create a favorable environment for the development of fungi.
The infection is also transmitted from an infected person. This often happens when someone in the family becomes infected with a fungus and the infection spreads to other family members.
Risk factors:
- Age - the older the person, the higher the risk of contracting onychomycosis. The largest percentage is occupied by the age category over 70 years. This is due to the fact that with age, nail growth slows down, and accordingly, fungi are not so effectively driven out.
- Wearing tight, uncomfortable shoes that cause your feet to sweat a lot.
- Walking without light shoes in public places such as swimming pools, showers and baths.
- Nail injury.
- The presence of skin diseases that affect the nails.
- Presence of diabetes mellitus.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Weakened immunity.
Symptoms of foot fungus
The main signs of fungus on the nails can be detected with the naked eye. These include the following nail changes:
- thickening - this occurs due to keratinization of the nail bed;
- color change - color can be different: white, gray, yellow, brown;
- increased fragility and destruction;
- discoloration - the color becomes dull;
- shape changes;
- purulent discharge from under the nail - may appear with an advanced form of onychomycosis;
- unpleasant smell.
The more precise symptoms of toenail fungus depend on the form of infection.
The infection can also affect the fingernails, but such onychomycosis is rare, since wearing shoes creates more suitable conditions for the development of infection.
Classification of onychomycosis
Today, two classifications of infection are relevant: according to the location of the infection and according to the principle of development.
According to localization, nail fungus can be:
Distal-lateral - the most common form, in which the side and front of the nail separates from the nail bed. The nail plate becomes less transparent and acquires a whitish or yellow color. Gradually, the edge of the nail begins to become thinner and crumble. As the infection progresses, it can reach the matrix, which can cause nail dystrophy.
Superficial - as a rule, the infection develops only on the surface layer of the nail and most often affects the big toe. White spots appear on the nails, as well as white stripes. As the spots develop, they begin to occupy most of the nail, and their color changes to yellow. When palpated, the nail feels rough.
Proximal - a white spot appears in the area of the white arch and base of the nail, from where it spreads to the front. As the infection develops, it grows to the deep layers of the plate, which leads to its destruction.
Total dystrophic - develops as a result of other forms, usually distal. The nail becomes yellowish-gray and thickened. Its surface becomes uneven and can also collapse, either partially or completely.
According to the principle of development, the fungus can be:
Normotrophic - changes relate only to the color of the nail plate; whitish or yellow spots appear on it. Over time, the entire nail may have this color. At the same time, the properties of the nail remain unchanged - they do not lose their shine and do not become thinner.
Hypertrophic - the nail loses its shine, its stratum corneum thickens and becomes deformed. It may be partially destroyed. Patients may experience pain while walking.
Atrophic, or onycholytic - in the place where the fungus develops, the nail plate becomes brownish-gray, and it is also torn away from the nail bed.
Why is nail fungus dangerous?
Often, nail fungus is associated only with a cosmetic problem. Changing the appearance of your nails can really cause aesthetic discomfort. In some patients, white or yellow nails due to infection may cause decreased self-esteem and a fear of showing off their legs in the pool or on the beach.
But as the fungus progresses, it becomes more dangerous, especially for people with diabetes, as it can lead to foot ulcers, gangrene and other dangerous conditions. Patients who are immunocompromised have an increased risk of contracting bacterial infections and are also at increased risk of an allergic reaction.
When to contact a specialist, and which doctor treats nail fungus
It is recommended to consult a specialist when the first symptoms of infection appear, since although the disease may develop slowly, as it progresses, treatment becomes more difficult and may take longer.
What is the name of the doctor who treats nail fungus?
Nail fungus is treated by a mycologist or dermatologist.
Diagnosis of nail fungus
At the appointment, the specialist collects anamnesis to determine the possible cause of the lesion and conducts a visual examination. To clarify the diagnosis, a microscopic examination of scrapings from the nails is performed. With its help, you can determine whether the change in the nail is a consequence of a fungal infection or the cause is other disorders.
Treatment of nail fungus
As part of the therapy, the doctor takes into account the form of the disease, the degree of damage to the nail, the well-being and age of the patient, as well as the rate of nail growth. Based on the information obtained, the following methods can be used:
External treatment
Refers to drug therapy and can be used as the only drug treatment option if the fungus has affected only a third of the nail in its front and sides. Patients are prescribed creams and varnishes with an antifungal effect. However, if the nail is deeply damaged, external medications may not work.
Drug therapy
If there is significant damage to the nail, patients are prescribed systemic antimycotics - antifungal drugs in the form of tablets or solutions that reach the site of infection through the blood.
If one medicine is ineffective, the doctor can choose another, since the effectiveness of the drugs is individual for each patient and it may take time to choose the most suitable one.
Drugs that stimulate the growth of nail plates can also be used.
A doctor must be responsible for the selection and prescription of a drug; self-medication may not produce results and may cause harm to health.
Treatment may be time-consuming and may require up to 12 months of antifungal medications.
Surgery
Patients may be recommended surgery - partial or complete removal of the infected nail. During therapy, the nail plate is separated from the bed, and the finger is covered with a sterile bandage.
Is it acceptable to treat toenail fungus with folk remedies?
On the Internet you can find various folk ways to cure foot fungus using herbs or homemade solutions. In fact, they help at most to slow down the development of infection in the initial stages, so the effectiveness of such remedies is controversial; it is better to consult a specialist.
Is it possible to completely cure toenail fungus?
Toenail fungus is difficult to cure - the therapy itself can take quite a long time, and relapses are common within 2-3 years after taking systemic antifungal agents. However, if all recommendations are followed and regular examinations by a doctor, there is a higher chance that the infection will not bother the patient in the future.
Prevention of toenail fungus
Recommendations before or during treatment for onychomycosis:
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene - regularly wash your feet, and if you have an infection, wash your hands after touching the nail. You should also change your socks regularly. If your feet often sweat, then, if possible, you should change your socks several times during the day.
- Trim your nails regularly - after the procedure, it is recommended to use a nail file to smooth the edges and slightly file thicker areas. After each haircut, nail scissors or clippers must be disinfected.
- Wear slippers when going to the pool, bathhouse and similar public places. After contact with water, dry the skin.
- Avoid uncomfortable shoes that cause your feet to sweat a lot.
- Regularly disinfect shoes with special sprays or solutions until the end of therapy.
- If the disease is confirmed, it is also important to make sure that the infection has not been transmitted to other family members.
Recommendations after treatment:
- Get rid of shoes that were worn during treatment.
- Lead a healthy and active lifestyle to strengthen your immune system.
- If symptoms appear after treatment, contact your doctor again.
Forecast
If you consult a doctor as soon as symptoms appear, you will be able to undergo treatment faster, avoid complications and, in most cases, completely cure the disease.